

Last PublicationsResearchers of the Complutense University in Madrid, Spain, investigated the effects of a synthetic CB1 receptor agonist on effects caused by stress in mice. Exposure to stress elicits damage and inflammation to nerve cells in the brain, contributing to cell death and damage in stress-related neurological and neuropsychiatric diseases. They found multifaceted neuroprotective effects of the cannabinoid which "suggest that CB1 activation could be a new therapeutic strategy against neurological/neuropsychiatric pathologies," which involve certain brain regions and a neuroinflammatory component in their aetiology. (Source: Zoppy S, et al. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Dec 8. ) Cannabis effective in the treatment of Tourette Syndrome and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) "German
scientists from the universities of Goettingen, Hamburg and Dresden
reported of the treatment of a 15-year-old boy with treatment
refractory Tourette Syndrome (TS) and attention deficit hyperactivity
disorder (ADHD) leading to severe physical and psychosocial impairment.
Administration of THC resulted in a considerable improvement of tics
without adverse effects, allowing parallel stimulant treatment of
comorbid ADHD. Along with THC treatment, intracortical inhibition, that
is inhibition of signal transmission between nerve cells in the cortex
of the brain, was increased."
"These
observations (...) suggest that the CNR1 (cannabinoid receptor gene)
gene may be a risk factor for ADHD and possibly PTSD, and that this
gene warrants further investigation for a role in neuropsychiatric
disorders"
Cannabis Improves Symptoms of ADHD, P. Strohbeck-Kuehner and al., Cannabinoids (2008 Mar.) "the
effects of cannabinoids in [ADHD]
patients may be different from those in healthy users suggesting an
involvement of the central cannabinoid receptor system in the
pathology of the [ADHD] disorder"
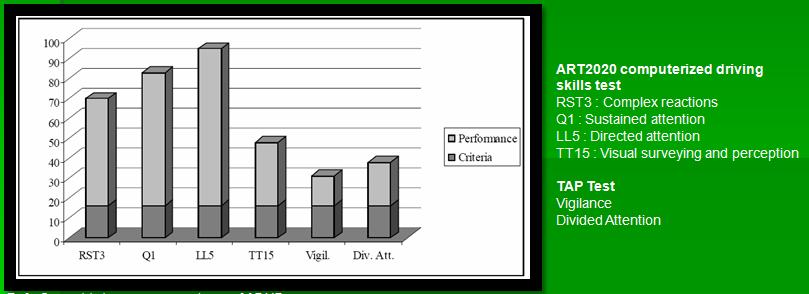 |